Vertical Spread Option Trading Strategy ,Types,Examples
Stock market trading requires patience, perseverance, and of course, the right strategy to succeed. In this context, it is worth mentioning that there are numerous trading techniques and strategies that you can use to maximize your gains in the markets. One of them is vertical spread option trading, a plan that involves the simultaneous trading of two options.
What does it mean and how can it help you? Let us simplify it below.
Introduction to Vertical Spread Options Trading
By vertical spread, we mean a trading blueprint that essentially involves trading two options simultaneously. Here are some key components of the trade that are worth knowing about:
- A trader buys and sells one option with a higher strike price and also another with a lower strike price. So, by trading two options at the same time, you’re taking a long and short position simultaneously.
- Both have the same expiration dates and since the options are vertically piled in the options chain, the trade is called vertical spread. If the spread did not have the same expiration dates, it would be called a calendar spread, which is a completely different trading approach.
- You can leverage this method to gain from what we call directional bias in the market. The technique helps you profit from trends in the market, while also reducing risks simultaneously.
- The basic types of vertical spreads are bulls and bears. The former involves bull call and put spreads where traders buy the option with a lower strike price and sell the option with the higher strike price (both methods).
- While bulls are more for those who are bullish about the market, the latter strategy is for a more bearish outlook of traders. In this case, they will sell options with lower strike prices and buy options with higher strike prices. The two sub-categories are thus the bear call and bear put spreads.
Now that you’ve got a basic idea, let us explore the two types of vertical spreads in slightly more detail.
Types of Vertical Spreads
The two main kinds of vertical spreads are the following:
|
Types of Vertical Spreads |
|
|
Bulls |
Bears |
|
Bull call and put spreads are usually a favourite for traders who are bullish by nature |
Traders adopting a bearish outlook usually leverage bear put or call spreads |
|
They purchase lower strike price options and sell higher strike price options |
They sell the lower strike price option and buy the higher strike price option |
The key difference is the cash flow timing, not including the differences in types of options |
The bear call spread may lead to a net credit to the account of the trader |
|
The bull call spread may initially lead to a net credit unlike the bull put spread |
The bear put spread, on the other hand, may lead to a net negative |
Vertical Spread P&L Calculation
There are diverse criteria for calculating P&L (profit and loss) of the vertical spreads option trading blueprint. These include the following:
|
Criteria |
Key Aspects |
|
Options’ strike prices |
Buying and selling options with multiple strike prices is a part of the strategy |
|
Premium paid/received |
Whenever any option is sold or bought, the premiums are received/paid (representing the price of options) |
|
Expiration date of options |
Options will always have a set date of expiration, after which they will lose their whole value |
To work out the profit/loss from the strategy, here’s what you need to do:
- Maximum Loss Calculation - The difference between the premiums paid and those received.
- Breakeven Point - The price at which you start generating profits.
- Final Calculation - The final profit and loss calculation will depend on the difference between the breakeven point and the price of the asset at the time of expiration. If the latter is higher than the threshold for breakeven, then the approach is profitable. Otherwise, if it goes below the threshold, it is a loss-making approach.
Example of Vertical
Let’s check out a relatable example that will help you understand what we’ve gone on about.
To give you an example, let us first make the following assumptions:
- You pay Rs. 10 in premium to buy a call option with a strike price of Rs. 200.
- You also gain Rs. 5 in premium by selling a similar call option with the strike price standing at Rs. 220.
What’s the end result?
- The highest loss in this case would be Rs. 5 (difference in premiums paid and received).
- The strike price of the call option bought and the net premium you paid would then be Rs. 205 and it can be taken as the breakeven point.
- The profit in this case will be Rs. 15 (difference between the sold call option strike price and breakeven point) if the underlying asset price holds at the time of expiration.
Here are some more examples of strategies/positions that you can also consider.
-
Butterfly Spread
This option strategy combines multiple bear and bull spreads. Traders combine four options contracts with the same expiry date at three strike points. Two options contracts are purchased (one at a higher and one at a lower strike price) and two are sold at a strike price that is in between. Here, the difference between the high and low strike price equates to the middle strike price.
Long Call Butterfly Spread
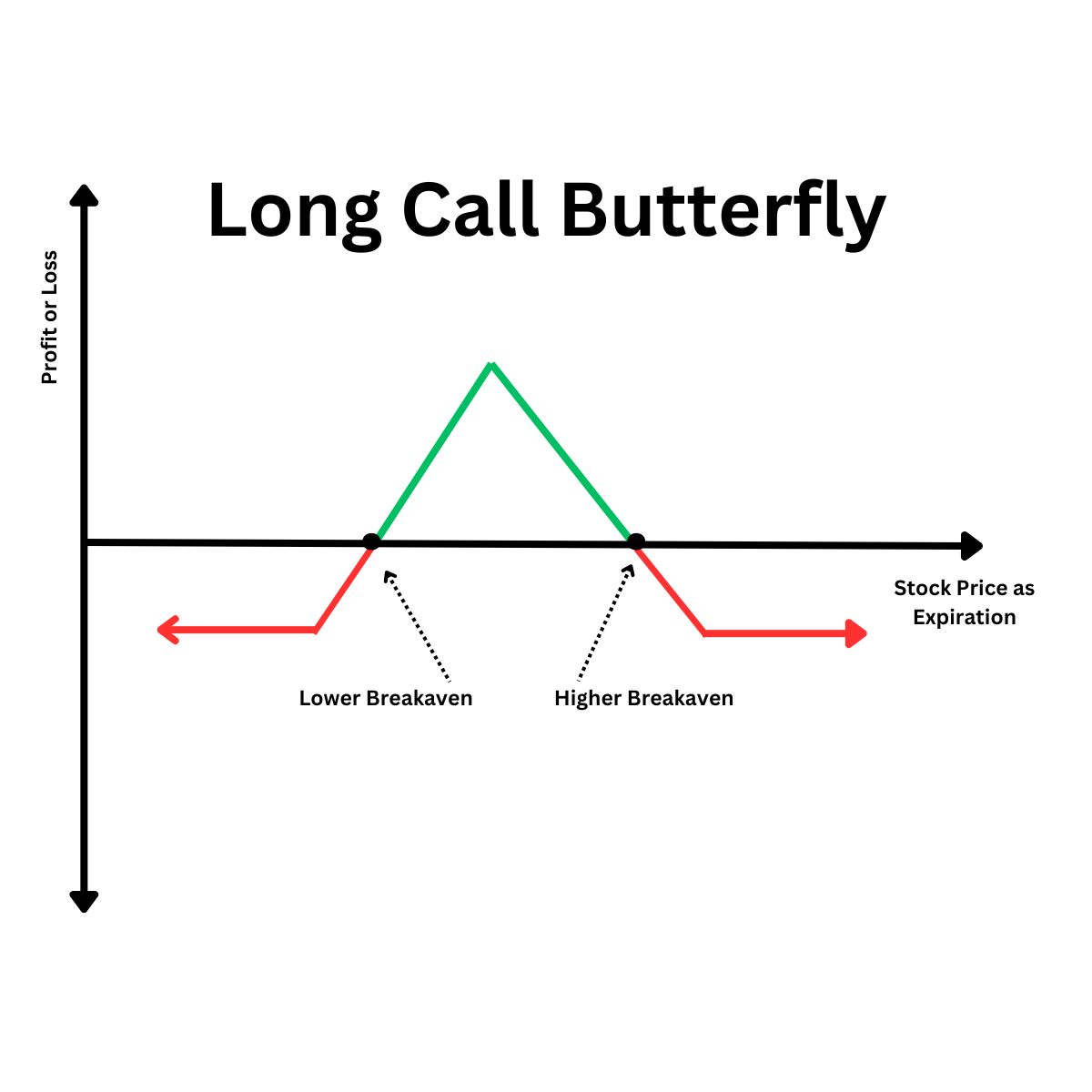
You believe that the stock of a company will stay stable over the next month and it is presently trading at Rs. 50.
- Buy a call option with a strike price of Rs. 45
- Sell two call options with a strike price of Rs. 50
- Buy one call option with a strike price of Rs. 55
At the time of expiry, if the stock price stays between Rs. 50-55, then you will earn a profit.
Short Call Butterfly Spread
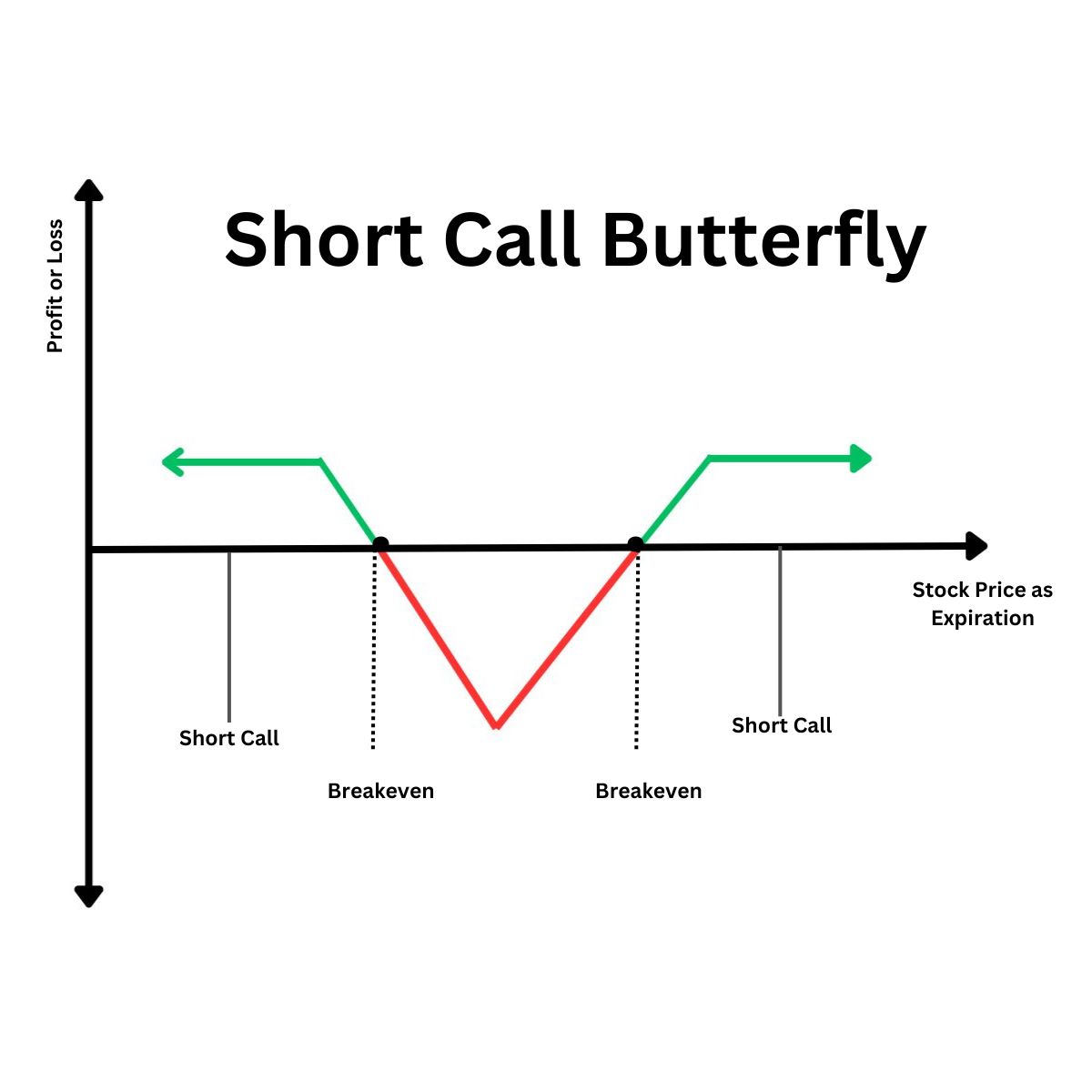
If you’re expecting major price movements for a stock trading at Rs. 60 per share and don’t known in which direction it will go, here’s what you can do:
- Sell a lower strike call option (at Rs. 55)
- Buy two middle strike call options (at Rs. 60)
- Sell one higher strike call option (at Rs. 65)
It helps you cap your potential losses while being able to benefit from volatility as well. Your maximum loss in this example will be only Rs. 2 per share.
Long Put Butterfly Spread
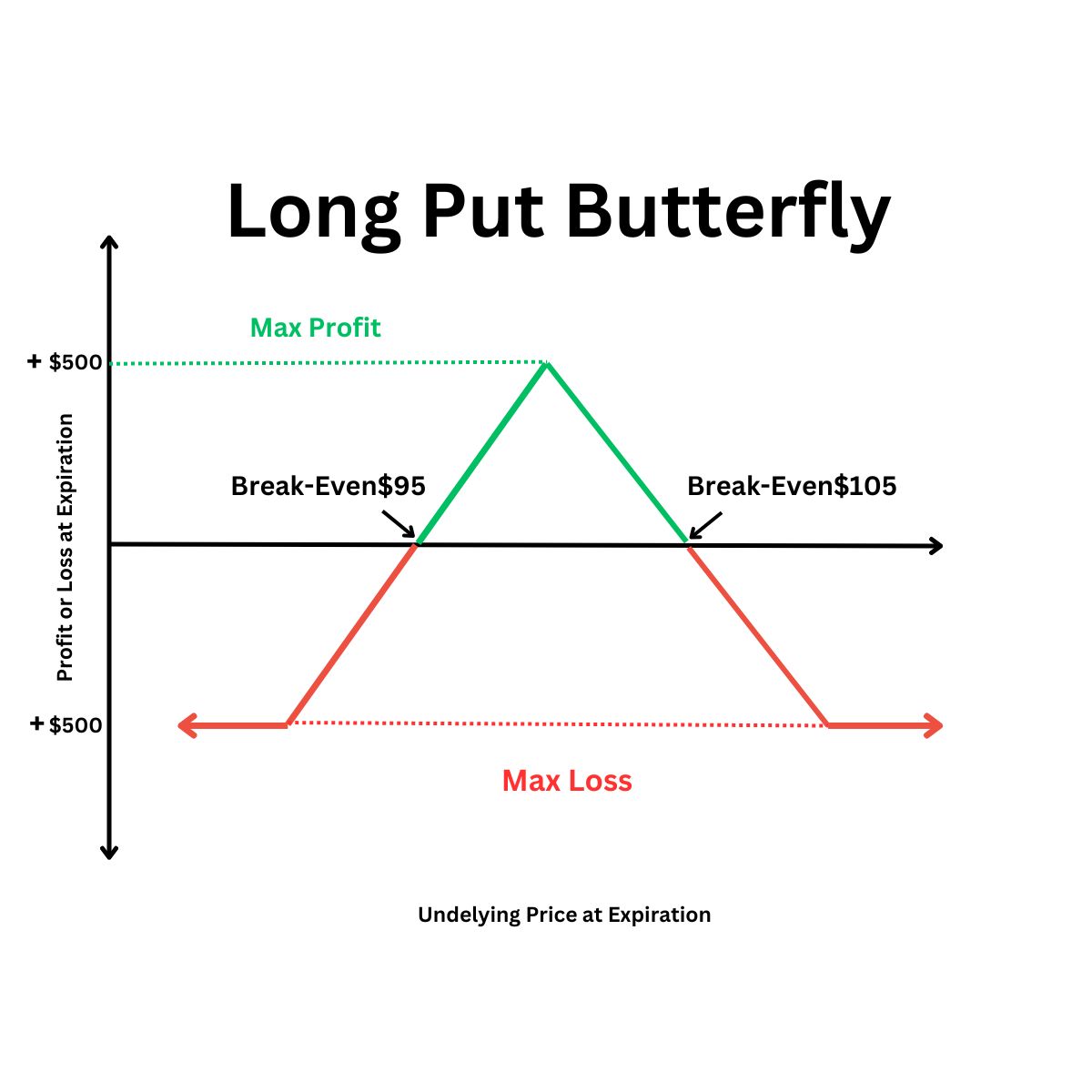
When you expect a major downward movement in the price of the asset, then you can do the following:
- Buy one higher strike put option
- Sell two middle strike put options
- Buy one lower strike put option
Short Put Butterfly Spread
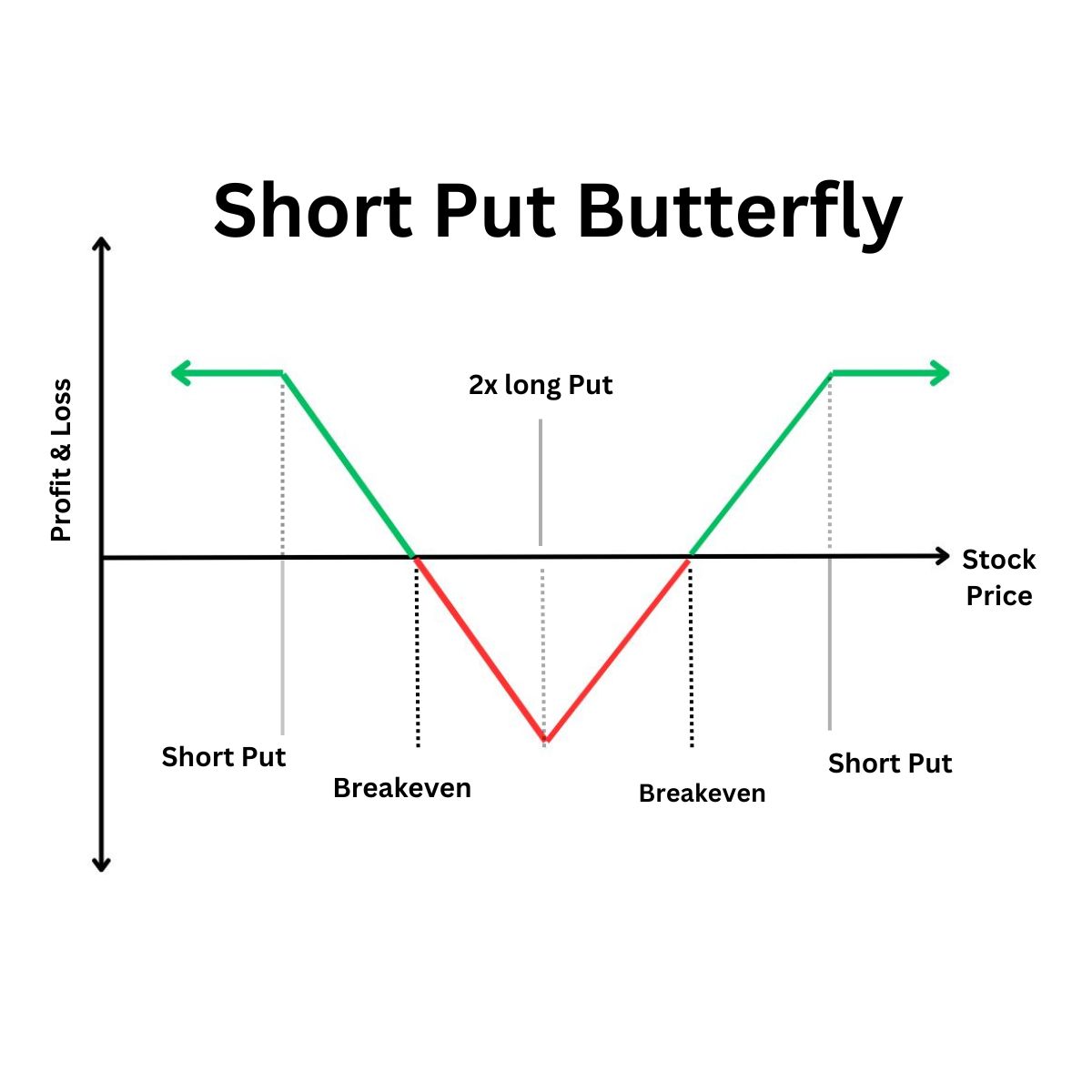
It is quite like the short call butterfly strategy, where you sell one in-the-money put option and buy two at-the-money put options. You can then sell one out-of-the-money put option.
-
Back Ratio
This is a strategy where you sell a smaller number of options and purchase a larger number of options to build a protective stance with lower downside risks. At the same time, there’s still potential for upside profit in case the underlying price of the stock moves in your chosen direction. The common ratio is 1:2, i.e. selling one in-the-money option for every two out-of-the-money options that you purchase.
Suppose you have a bearish outlook on the underlying stock asset and want to structure a back spread that will benefit from a stock decline. You can thus purchase two put options contracts and then sell short your put contract option to get the premium.
-
Iron Condor
The strategy has a neutral direction and benefits from a stock that is trading in a range through the expiry of the options. You have to sell the bullish spread and bearish spread simultaneously and profit from the stock price landing between these strikes at expiry.
You can employ this strategy by selling OTM (over-the-money) call and put options while buying more OTM call and put options simultaneously. Suppose a stock price is Rs. 400. You can sell a put option at a strike price of 397.5 and a call option with a strike price of 402.5. To lower the loss potential, you can also buy a put option for Rs. 395 and a call option for Rs. 405. This will thus form the core of your strategy with variable payoffs, depending on market movements.
Will it Work for You?
So, to come to the core question- when does vertical spread option trading work for you? Here are some key aspects worth noting in this regard.
- It works if you want a low-risk technique that lets you profit from trends in the market, while lowering potential losses.
- Successful implementation of this technique requires you to be knowledgeable about options trading and the underlying risks.
- This strategy works better if you feel that the market will either increase/decrease considerably over a period of time.
- You can benefit from two scenarios with this strategy- one where the stock price goes up and another where it falls. The only way you make a loss is where the stock price remains stagnant, which is not as likely in the case of options.
- The approach is also worth trying if you’re inclined towards speculating/hedging on stocks without any interest in them until they either go up/down by a particular amount.
Concluding Notes
Vertical spread option trading can be a viable approach if done smartly and in specific scenarios as outlined above. Of course, as with any investment strategy, it pays to be aware of the underlying risks and market trends.
Disclaimer: This content is solely for educational purposes. The securities/investments quoted here are not recommendatory.