What is a Synthetic Put Strategy?
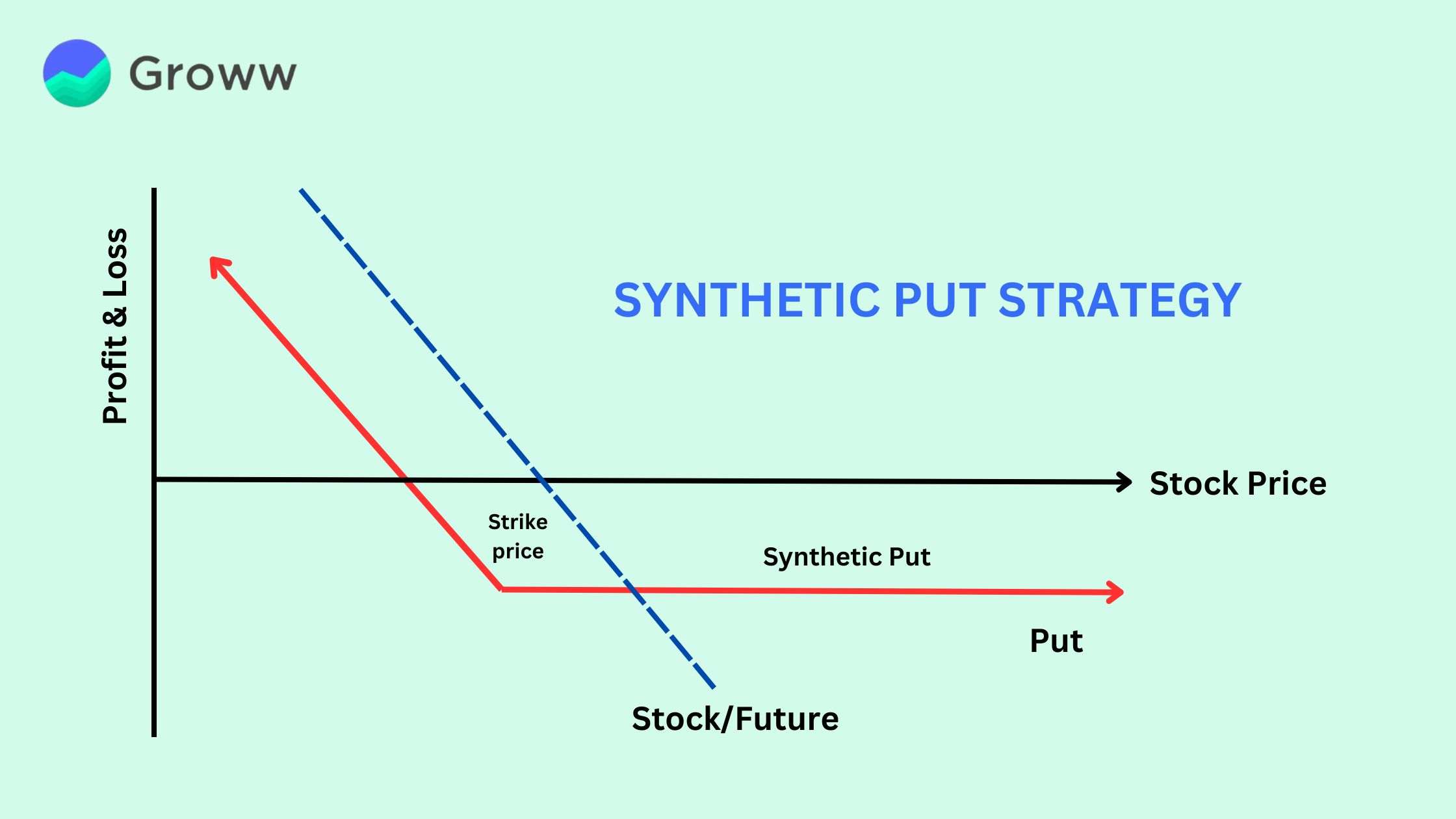
A synthetic put is an options strategy that replicates a long put position by combining a short stock trade with a long call option on the same stock. This approach involves an investor holding a short stock position while purchasing an at-the-money (ATM) call option for protection. The goal is to hedge against potential price increases in the stock.
Since the payoff structure mirrors a long put, this strategy is known as a ‘synthetic’ put. It is also known as a married call and a protective call. To learn more about the synthetic put strategy, keep reading.
When to Use a Synthetic Put?
A synthetic put is primarily used as a capital-preserving strategy rather than a profit-making one. The cost of the call option (the option premium) is built into the strategy, which can reduce its profitability if the underlying stock moves in the desired direction.
Synthetic puts are typically used as a form of protection against short-term price spikes in a generally bearish stock or as a safeguard against unexpected upward movements in stock price.
For newer investors, synthetic puts offer a safety net by limiting potential losses, which can provide more confidence as they explore different investment strategies. However, it is important to note that any form of protection comes at a cost, which may include the price of the option, commissions and other fees.
Things to Consider Before Using a Synthetic Put Strategy
A synthetic put strategy is designed to manage risk by adjusting a trade’s structure. If market conditions shift unexpectedly, investors can modify their positions using synthetic options rather than purchasing or shorting additional stock. This flexibility helps lower trading costs and capital requirements. However, it’s important to note that while this strategy provides downside protection, it also limits the maximum potential profit from the original trade. Weigh the advantages and drawbacks carefully before implementing a synthetic position.
Benefits of Using a Synthetic Put Strategy
Incorporating synthetic puts into your trading strategy offers several advantages:
- Hedges Against Sharp Price Increases: This strategy helps protect your position if the underlying stock experiences a sudden surge in price.
- Flexibility in Adjusting Trades: You can modify your market outlook without needing to exit your initial short position.
- Reduces Transaction Costs: Since fewer trades are required to adjust your position, you can minimise trading fees and expenses.
Example of Synthetic Put Strategy
Since short selling in the cash market is limited to intraday trades, you can use futures to take a short position while simultaneously buying call options. This creates a synthetic put position, mimicking the payoff of a long put option.
Suppose the following is the market condition:
- Current stock price: ₹2,500
- 1-month futures price: ₹2,520
- Expiry: 30 days
The following are the steps to be taken to set up the trade:
- Sell 1 futures contract at ₹2,520 per share, with a lot size of 500 shares.
- Buy 5 call option contracts with a strike price of ₹2,520, each covering 100 shares, by paying a premium of ₹70 per share.
Your total premium cost = ₹70 × 100 × 5 = ₹35,000.
Additionally, you will need to maintain a margin to hold the futures position. The exact amount depends on your broker and market conditions. So be sure to check the latest requirements before placing your trade.
The following are the potential outcomes at expiry:
Scenario 1: Futures Price Rises to ₹2,700
- Loss on futures contract: 500 × (₹2,700 – ₹2,520) = ₹90,000
- Profit on call options: 500 × (₹2,700 – ₹2,520 – ₹70) = ₹55,000
- Net loss: ₹90,000 – ₹55,000 = ₹35,000
Scenario 2: Futures Price Drops to ₹2,300
- Profit on futures contract: 500 × (₹2,520 – ₹2,300) = ₹1,10,000
- Loss on call options (premium paid): ₹35,000 (since the options expire worthless)
- Net profit: ₹1,10,000 – ₹35,000 = ₹75,000
Scenario 3: Futures Price Stays at ₹2,520
- No gain or loss on the futures contract
- Loss on call options (premium paid): ₹35,000
- Net loss: ₹35,000
By using a synthetic put strategy, you can hedge your position while replicating the risk-reward profile of a long put option. Understanding these scenarios helps you manage risks and make informed trading decisions.
Conclusion
The synthetic put strategy is useful for traders looking to hedge against unexpected price increases while maintaining a short position. While it offers protection against sharp price movements, traders should consider the associated costs, such as option premiums and brokerage fees. Understanding the mechanics and potential outcomes of the synthetic put strategy can help investors make more informed decisions and manage risks effectively.
|
Disclaimer: This content is solely for educational purposes. The securities/investments quoted here are not recommendatory. |